A new report illustrates how groundwater pumping can affect the amount of water available in streams within the Malad-Lower Bear River Area in Utah. The product was developed by the U.S. Geological Survey, in cooperation with the Utah Department of Natural Resources, Division of Water Rights.
articles
Consumer behaviour causing premature deaths from air pollution
A UBC researcher is drawing attention to the human cost of our consumer behaviour by examining the number of deaths caused by air pollution from manufacturing goods. While some countries bear the brunt of the health risks from air pollution, the products often end up in the hands of consumers in other countries.
Lightform: The Magical Little Device That Transforms Whole Rooms Into Screens
Technology wants to disappear. In computing’s early days, the machines swallowed entire rooms. Today, we wear them on our wrists. Soon, they could vanish completely, their smarts embedding directly into our surroundings.
Wildlife Safari Defends Its Elephant Car Wash
During the summer at the Wildlife Safari zoo in Oregon, visitors can pay $25 to have elephants “wash” their vehicles. The elephants use their trunks as sponge holders and hoses.
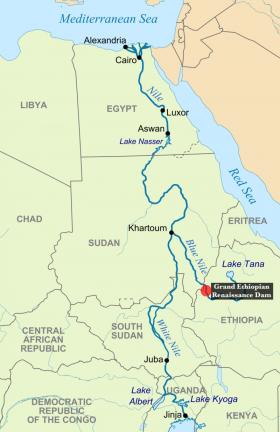
The Vanishing Nile: A Great River Faces a Multitude of Threats
The Nile River is under assault on two fronts – a massive dam under construction upstream in Ethiopia and rising sea levels leading to saltwater intrusion downstream. These dual threats now jeopardize the future of a river that is the lifeblood for millions.
When peaceful coexistence turns into concurrence
To find out how rising temperatures could affect species diversity, biologists from the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv) and the Leipzig University have developed a simple experiment: they covered the bottom of different Petri dishes with litter material, then put in two species of springtails, that is, arthropods only a few millimetres in size, and then added mites feeding on springtails. Subsequently, for some of the Petri dishes they increased the ambient temperature from originally 13.5°C to 18.5°C and for some other Petri dishes to 23.5°C. In those Petri dishes, the temperatures were hence five, respectively ten degrees higher than the conditions to which the animals had been exposed to in long-term cultures over years. This created simplified miniature ecosystems under climate change conditions, in which the springtail species that peacefully coexist in the wild represented the prey, and the mites represented the predators. For two months, the researchers then observed how the interactions between the three species would develop with different temperatures.