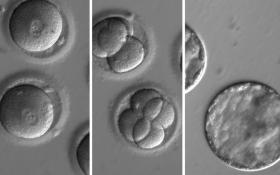
A Métis student in the University of Saskatchewan School of Public Health, Adams is one of 16 young leaders from across Canada appointed to the Your Energy Future program.
Participants in the year-long program, delivered in partnership by the Public Policy Forum and leadership development fellowship Action Canada, will become change-makers in Canada’s energy agenda. They develop strategies to prepare Canadian people, communities and governments to successfully transition to a low-carbon, clean energy future.