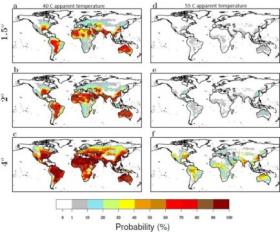
Heatwaves amplified by high humidity can reach above 40°C and may occur as often as every two years, leading to serious risks for human health. If global temperatures rise with 4°C, a new super heatwave of 55°C can hit regularly many parts of the world, including Europe.
articles
Climate change may confuse plant dormancy cycles
Perennial plants in the Midwest are well attuned to their surroundings. They hunker down all winter in a dormant state, just waiting for a sign that it’s safe to unfurl their first tender leaves or flower buds. For many plants, the cue is a sustained warming trend, but day length also factors into the dormancy equation.
There's Still Time to Prepare Yourself for the Apoceclipse
For years, the total solar eclipse of August 21—the first to be visible in the mainland United States since 1979—has been in stealth mode. With the exception of the enthusiasts who’ve been snatching up all the hotel rooms along the eclipse’s 70-mile-wide, 2,800-mile-long path from Oregon to South Carolina, nobody really knew it was coming. But in the past few months, word of this spectacular natural phenomenon has spread like wildfire, and communities across the country that will be graced by the moon’s shadow are on high alert, anticipating millions of visitors.
RAVAN CubeSat Measures Earth's Outgoing Energy
An experimental small satellite has successfully collected and delivered data on a key measurement for predicting changes in Earth’s climate.
NASA's Smartest Satellite Is Gone. Can Private Space Replace It?
Look down on Buenos Aires from the sky, and you can learn a fair bit about the city. It's got a lot of concrete. Also a lot of trees. There's a bright green river delta to the north, which probably explains the ruddy-brown bay to the east. But with the right camera—a hyperspectral one—you can pick up a whole lot more. New colors emerge, hidden hues your eyes and mine aren't wired to see. And these colors reflect even more detail about the scene: the gases coming out of the city, the health of the plants surrounding it, the species of algae coloring the water offshore.
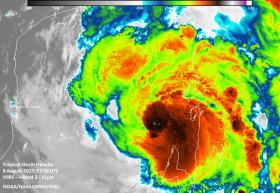
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP Satellite Takes a Double Look at Tropical Storm Franklin
When NASA-NOAA’s Suomi NPP satellite passed over Tropical Storm Franklin instruments aboard provided a night-time view of the storm’s clouds and measured their temperatures, revealing a strengthening storm.
The Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument aboard the NASA-NOAA Suomi NPP satellite captured infrared images of Franklin on August 8 at 3:58 a.m. EDT (0758 UTC). The Suomi NPP night-time image showed that Franklin’s northwestern edge had not yet reached San Francisco de Campeche or Merida, as the lights of both cities were still visible in the image. The infrared image provided temperatures of Franklin’s cloud tops, where thunderstorms surrounding the low-level center were as cold as 190 Kelvin (minus 117.7 degrees Fahrenheit / minus 83.1 degrees Celsius). NASA research has shown that storms with cloud top temperatures that cold have the ability to generate very heavy rainfall.