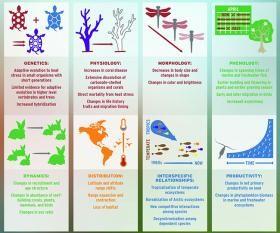
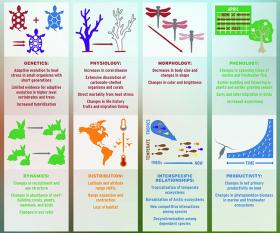
A full 30 percent of the world’s electricity generation comes under the umbrella of just nine energy companies, and they have just joined forces to ramp up technology investments aimed at decarbonization. The global, collaborative effort was announced earlier this week by the companies’ nonprofit organization, the Global Sustainable Electricity Partnership.
To be clear, the decarbonization announcement leaves plenty of wiggle room for “clean” coal and natural gas, at least in the near future. However, a look at the group’s sole U.S. member, American Electric Power, demonstrates that a Republican administration cannot stop the global transition to low and zero-carbon electricity.