Palm trees have been synonymous with Los Angeles for decades, appearing on everything from tourism ads to movie posters. But now, LA’s iconic trees are dying from a fatal fungus and an invasive beetle, as well as simply from old age, and the city doesn’t have any plans to revive them, according to Los Angeles Times.
articles
Clearing the air
This past June, Grace Li '17 stepped off a plane in Paris ready to spend her summer tracking down a silent killer. Now Li, her former teammates, and the flock of trained pigeons who also contributed to the project are about to get closer to their goal.
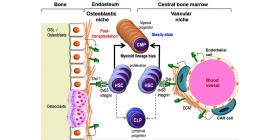
Bone Marrow Protein May Be Target for Improving Stem Cell Transplants
Bone marrow contains hematopoetic stem cells, the precursors to every blood cell type. These cells spring into action following bone marrow transplants, bone marrow injury and during systemic infection, creating new blood cells, including immune cells, in a process known as hematopoiesis.
Annual Southern Sea Otter Survey: Despite Small Population Dip, Species Moves a Step Closer to Recovery
According to data released Friday by the U.S. Geological Survey and partners, the three-year average of the total counts of southern sea otters was down from last year’s high, although it still exceeded the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service’s delisting threshold for a second straight year.
Hunt is over for one of the 'Top 50 Most-Wanted Fungi'
In a step toward bridging the gap between fungal taxonomy and molecular ecology, scientists from several institutions including Los Alamos National Laboratory have characterized a sample of “mystery” fungus collected in North Carolina and found its home in the fungal tree of life.
Puerto Rico facing disaster of major proportions
A week after Hurricane Maria rolled through Puerto Rico, the island faces a public health crisis with no power and a growing shortage of drinking water and food.