Adding milkweeds and other native flowering plants into midwestern agricultural lands is key to restoring monarch butterflies, with milkweed sowers from all sectors of society being critically needed for success.
articles
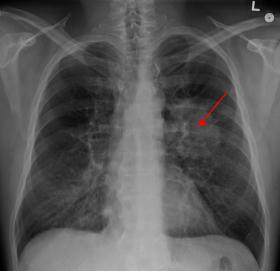
Lung cancer screening could save money as well as lives, research shows
Lung cancer screening is likely to be cost-effective, particularly if it also identifies other tobacco-related conditions in high-risk people, suggests new research published in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology (JTO).
New study explores plant adaptations to drought and cold stress
Recent advances in technology have allowed scientists to probe the molecular nature of life, analyzing thousands of genes at a time and recognizing patterns of gene interaction. In a recent paper published in Proceedings of the Royal Society B, complexity scientist Samuel Scarpino and co-authors explore gene co-expression networks that have evolved to help plants withstand drought and cold.
Bumble bees make a beeline for larger flowers
Bumble bees create foraging routes by using their experience to select nectar-rich, high-rewarding flowers. A study by Shohei Tsujimoto and Hiroshi Ishii of the University of Toyama in Japan now suggests that bees actually forage more efficiently when flower sizes are large rather than small. This indicates that for these insect pollinators foraging quickly is more efficient than foraging accurately. The research is published in Springer’s journal Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology and uses a laboratory-based experiment to investigate how aspects of associative learning influence how bumble bees find food among different-sized flowers.
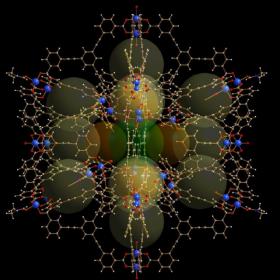
Scientists build giant 'molecular cages' for energy conversion and drug delivery
Scientists from Trinity College Dublin and AMBER, the Science Foundation Ireland-funded materials science research centre hosted in Trinity College Dublin, have created ‘molecular cages’ that can maximise the efficiency of converting molecules in chemical reactions, and that may in future also be used as sensors and drug-delivery agents. The cages can be packed with different molecules, many of which have a specific task or functionality.
Nationwide study of U.S. seniors strengthens link between air pollution and premature death
A new study of 60 million Americans—about 97% of people age 65 and older in the United States—shows that long-term exposure to airborne fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and ozone increases the risk of premature death, even when that exposure is at levels below the National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) currently established by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
The Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health researchers found that men, blacks, and low-income populations had higher risk estimates from PM2.5 exposure compared with the national average, with blacks having mortality risks three times higher than the national average.