In their work toward 3-D printing transplantable tissues and organs, bioengineers and scientists from Rice University and Baylor College of Medicine have demonstrated a key step on the path to generate implantable tissues with functioning capillaries.
articles
Reconciling predictions of climate change
Harvard University researchers have resolved a conflict in estimates of how much the Earth will warm in response to a doubling of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. That conflict — between temperature ranges based on global climate models and paleoclimate records and ranges generated from historical observations — prevented the United Nations’ Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) from providing a best estimate in its most recent report for how much the Earth will warm as a result of a doubling of CO2 emissions.
NASA Gives Eastern Pacific Ocean's Hurricane Eugene 'Eye Exam'
NASA satellites gave the Eastern Pacific Ocean's Hurricane Eugene an "eye exam" as it studied the storm in infrared and visible light. NASA satellite imagery taken at different times showed Eugene's eye open and closed.
Stanford researchers observe unexpected flipper flapping in humpback whales
When Jeremy Goldbogen, an assistant professor of biology at Stanford University, affixed recording devices to humpback whales, it was with the hope of learning more about how the animals move in their natural environment – deep underwater and far from human’s ability to observe.
Kansas State University researchers help with landmark study of wild wheat ancestor
Kansas State University scientists are part of a breakthrough study in which an international team of researchers has successfully deciphered all 10 billion letters in the genetic code of a wild ancestor of wheat.
Their work is published in the July 7 issue of Science Magazine.
“The relative of wheat is called wild emmer, which is one of the founding crops of human society,” said Eduard Akhunov, professor of plant pathology and wheat genomics at Kansas State University. “Wild emmer was one of the first crops that was domesticated 10,000 years ago, which was a critical step in moving from hunting and gathering to an agricultural society.”
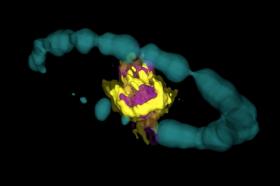
Heart of an Exploded Star Observed in 3-D
Supernovas — the violent endings of the brief yet brilliant lives of massive stars — are among the most cataclysmic events in the cosmos. Though supernovas mark the death of stars, they also trigger the birth of new elements and the formation of new molecules.