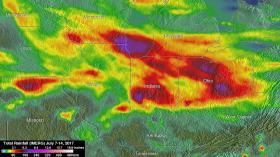
Heavy rain resulted in significant flooding in the U.S. Midwest over the week of July 7 to 14, 2017. Using satellite data, NASA estimated the amount of rain that fell over those areas and used satellite data to create 3-D imagery of severe storms.
NASA's Integrated Multi-satellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) data were used to show estimates of rainfall accumulation in the Midwest during the period from July 7 to 14, 2017. The analysis was conducted at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, and indicates that parts of Wisconsin, Illinois, Indiana and Ohio had the highest rainfall totals during the period with more than 6 inches (152.4 mm) of rain being seen in many areas.