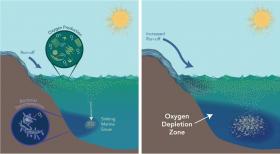
The living, breathing ocean may be slowly starting to suffocate. More than two percent of the ocean’s oxygen content has been depleted during the last half century, according to reports, and marine “dead zones” continue to expand throughout the global ocean. This deoxygenation, triggered mainly by more fertilizers and wastewater flowing into the ocean, pose a serious threat to marine life and ecosystems.
Yet despite the critical role of oxygen in the ocean, scientists haven’t had a way to measure how fast deoxygenation occurs—today, or in the past when so-called major “anoxic events” led to catastrophic extinction of marine life.