Burlington, ON – IKEA Canada has signed agreements to acquire an 88MW wind farm located near Drumheller, Alberta approximately 130km east of Calgary. Consisting of 55 turbines, the Wintering Hills wind farm will generate 275 million kWh (kilowatt hours) of energy, the equivalent to the electricity consumption of 54 IKEA stores or nearly 26,000 Canadian households.
articles
Nordic countries are bringing about an energy transition worth copying
What can we learn from the Nordic low-carbon energy transition given the new US leadership vacuum on climate change? A new study by Professor Benjamin Sovacool at the University of Sussex offers some important lessons.
The Trump administration's "First energy plan" criticises the "burdensome" regulations on the energy industry and aims to eliminate "harmful and unnecessary policies such as the Climate Action Plan" which was introduced by President Barack Obama. It has also deleted all mentions of climate change and global warming from the White House website.
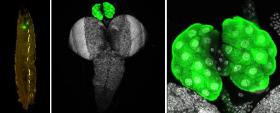
How Insects Decide to Grow Up
Scientists discover key mechanism that controls when fruit flies sexually mature
Like humans, insects go through puberty. The process is known as metamorphosis. Examples include caterpillars turning into butterflies and maggots turning into flies.
But, it has been a long-standing mystery as to what internal mechanisms control how insects go through metamorphosis and why it is irreversible.
New tool helps oyster growers prepare for changing ocean chemistry
For Bill Mook, coastal acidification is one thing his oyster hatchery cannot afford to ignore.
Mook Sea Farm depends on seawater from the Gulf of Maine pumped into a Quonset hut-style building where tiny oysters are grown in tanks. Mook sells these tiny oysters to other oyster farmers or transfers them to his oyster farm on the Damariscotta River where they grow large enough to sell to restaurants and markets on the East Coast.
The global ocean has soaked up one third of human-caused carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions since the start of the Industrial Era, increasing the CO2 and acidity of seawater. Increased seawater acidity reduces available carbonate, the building blocks used by shellfish to grow their shells. Rain washing fertilizer and other nutrients into nearshore waters can also increase ocean acidity.
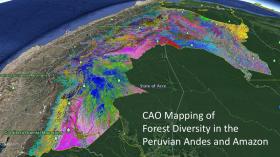
High-Tech Maps of Tropical Forest Diversity Identify New Conservation Targets
New remote sensing maps of the forest canopy in Peru test the strength of current forest protections and identify new regions for conservation effort, according to a report led by Carnegie’s Greg Asner published in Science.
Asner and his Carnegie Airborne Observatory team used their signature technique, called airborne laser-guided imaging spectroscopy, to identify preservation targets by undertaking a new approach to study global ecology—one that links a forest’s variety of species to the strategies for survival and growth employed by canopy trees and other plants. Or, to put it in scientist-speak, their approach connects biodiversity and functional diversity.
Researchers Work to Restore the Long-Lost Flavor of Tomatoes
New research reveals which genes are needed to reinstate the rich, original flavor of tomatoes, now absent in many grocery shelf varieties of this fruit. The results are published in the 27 January issue of Science.