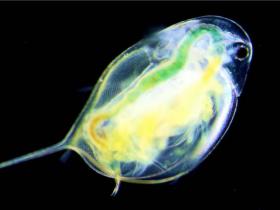
Can environmental toxins disrupt circadian rhythms – the biological “clock” whose disturbance is linked to chronic inflammation and a host of human disorders? Research showing a link between circadian disruption and plankton that have adapted to road salt pollution puts the question squarely on the table.
articles
New engine optics to fuel future research
A new optical device at Sandia National Laboratories that helps researchers image pollutants in combusting fuel sprays might lead to clearer skies in the future.
Agricultural Productivity Drove Euro-American Settlement of Utah
On July 22, 1847, a scouting party from The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints stood above the Great Salt Lake Valley in modern-day Utah; by 1870, more than 18,000 followers had colonized the valley and surrounding region, displacing Native American populations to establish dispersed farming communities. While historians continue to debate the drivers of this colonization event, a new study from the University of Utah proposes that agricultural productivity drove dispersal patterns in a process that led the current distribution of Utah populations today.
MIPT scientists enlist lichens to monitor air pollution
Researchers have shown free radical concentrations in lichens to be directly related to air pollution.
In Pursuit of a Universal Flu Vaccine
Flu shot season is here. But as you head to the doctor’s office or pharmacy to get vaccinated, scientists are working to make this yearly ritual a thing of the past. Researchers around the world, including at the University of Rochester Medical Center (URMC), are pursuing a “universal” flu vaccine, one that would protect against most or all seasonal and pandemic strains of the flu virus.
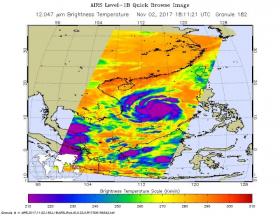
NASA Sees Damrey Strengthen into a Typhoon
NASA’s Aqua satellite and the NASA-NOAA Suomi NPP satellite provided imagery of Damrey as it strengthened into a typhoon in the South China Sea.