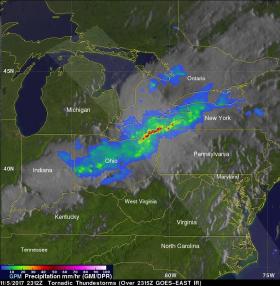
Severe weather that rolled through the Ohio Valley on Nov. 5 was analyzed by NASA's Global Precipitation Measurement mission or GPM satellite. GPM provided forecasters at the National Weather Service with rain rates and cloud heights that showed where strongest storms were located.
articles
Federal climate science report for U.S. released
U.S. Global Change Research Program’s (USGCRP) Climate Science Special Report (CSSR), which serves as Volume I of the Fourth National Climate Assessment (NCA4), describes current trends in the climate globally and for the U.S., and projects trends in temperature, precipitation, sea-level rise and Arctic sea ice for the remainder of this century.
Higher Air Pollution in Cities Tied to Higher Mortality
New research presented today at APHA’s 2017 Annual Meeting and Expo examined the burden of air pollution and its association with mortality in Chinese cities. The study by researchers at Drexel University Dornsife School of Public Health showed a significant correlation between higher air quality index concentrations and higher mortality rates. The study is the first to provide strong evidence of the burden of air pollution in major Chinese cities, as well as the impacts of air quality and climate change on urban population mortality.
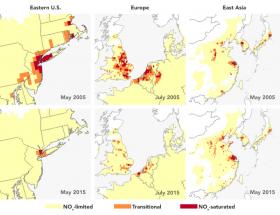
NASA Satellite Tracks Ozone Pollution by Monitoring Its Key Ingredients
Ozone pollution near Earth's surface is one of the main ingredients of summertime smog. It is also not directly measurable from space due to the abundance of ozone higher in the atmosphere, which obscures measurements of surface ozone. New NASA-funded research has devised a way to use satellite measurements of the precursor gases that contribute to ozone formation to differentiate among three different sets of conditions that lead to its production. These observations may also assist air quality managers in assessing the most effective approaches to emission reduction programs that will improve air quality.
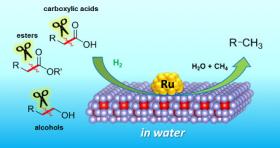
Breaking the Chain: Catalyzing a Green Future for Chemistry
The fight against climate change is a call-to-arms for industry. We currently rely on fossil fuels, a major source of the greenhouse gas CO2, not only for energy but also to create chemicals for manufacturing. To ween our economies off this dependency, we must find a new source of “green” raw materials so that factories and laboratories can run without producing and emitting CO2.
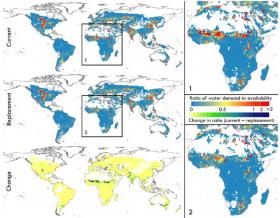
Swapping Where Crops are Grown Could Feed an Extra 825 Million People
Redrawing the global map of crop distribution on existing farmland could help meet growing demand for food and biofuels in coming decades, while significantly reducing water stress in agricultural areas, according to a new study. Published today in Nature Geoscience, the study is the first to attempt to address both food production needs and resource sustainability simultaneously and at a global scale.