The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service today proposed to protect 338,100 acres of critical habitat in Mississippi and Alabama for black pine snakes, whose southeastern, longleaf pine forests have been reduced to less than 5 percent of their historic extent. The snake depends on these forests, which are being lost to agriculture and pine plantations, fire suppression and urbanization. Black pine snakes were proposed for Endangered Species Act protection last fall as the result of a settlement agreement with the Center for Biological Diversity that speeds protection decisions for 757 imperiled species around the country.
articles
Warm Winter in Pacific Northwest means less snowpack and water worries
If it seemed like Oregon has had a lot of unseasonably warm days this winter, well, it’s because we have. Now the focus is on a very low snowpack – and the implications that may have later this year.
The meteorological winter – which is comprised of December, January and February – recently wrapped up and depending on where you live in Oregon, it was one of the warmest – if not the warmest – winters on record.
What inspires people to support conservation?
What inspires people to support conservation? As concerns grow about the sustainability of our modern society, this question becomes more important. A new study by researchers at Cornell University provides one simple answer: bird watching and hunting.
This survey of conservation activity among rural landowners in Upstate New York considered a range of possible predictors such as gender, age, education, political ideology, and beliefs about the environment. All other factors being equal, bird watchers are about five times as likely, and hunters about four times as likely, as non-recreationists to engage in wildlife and habitat conservation. Both bird watchers and hunters were more likely than non-recreationists to enhance land for wildlife, donate to conservation organizations, and advocate for wildlife-all actions that significantly impact conservation success.
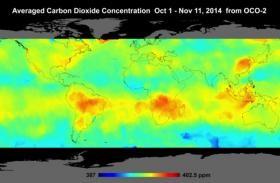
Mapas de la NASA de las emisiones de CO2 en todo el planeta
Ha sido necesario ocupar cinco meses del satélite más nuevo de la NASA, para monitorear el dióxido de carbono, haciendo hasta 1 millón de mediciones al día de cómo se mueve el dióxido de carbono en todo el planeta. Ahora los científicos de la NASA han compartido los primeros mapas globales creados con esos datos, que muestran una de las vistas más detalladas de CO2 jamás creados.
El satélite, conocido como OCO-2, ha estado en órbita desde julio...
Solar Impulse going around the world on sunshine
After 13 years of planning, the Solar Impulse SI2 took off last night from Al-Bateen Executive Airport in Abu Dhabi at 7:12 a.m. local time. This initiated the first leg of its historic attempt to be the first solar-powered airplane to fly around the world. If all goes well, the plane will return to Al-Bateen in June or July. As reported here in January, the first leg was a short 12-hour “shakedown cruise” to Muscat, Oman, piloted by Andre Borschberg. The plane landed safely in Muscat, more or less on schedule, at 12:14 p.m. Eastern time.
Of the two pilots who will take turns behind the wheel, Borschberg is the engineer and former fighter pilot who is intimately familiar with every detail of the plane’s design and construction.
Wetland restoration can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions
Restoration of wetlands can reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This is shown in a report that has been written in part by researchers from the University of Gothenburg. Former wetlands that have been drained and which are currently used for forestry and agriculture give off 11.4 million tons of carbon dioxide equivalents. That can be compared with Sweden's total emissions of 57.6 million tons (when the land use sector is not included). But in Sweden's report to the Climate Convention, emissions from drained peatland are not visible since they are included with forest growth.