Savannahs form one of the largest habitats in the world, covering around one-fifth of the Earth's land area. They are mainly to be found in sub-Saharan Africa. Savannahs are home not only to unique wildlife, including the 'Big Five' - the African elephant, rhinoceros, Cape buffalo, leopard and lion - but also to thousands of endemic plant species such as the baobab, or monkey bread tree.
articles
Monarch Butterflies Just Lost Another Third of Their Population
While international efforts are underway to protect iconic monarch butterflies from disappearing, the latest population count has found their numbers have dropped by nearly one-third since last year.
According to the Xerces Society for Invertebrate Conservation, in the 1990s, an estimated one billion monarchs embarked on an epic annual migration. Their journey takes them from sites in Canada and the U.S. to wintering grounds in California and Mexico, where they find shelter and warmth among oyamel fir trees in the winter.
Extraordinary Levels of Pollution Found in the Deepest Part of the Sea
Since the Mariana Trench is the deepest part of the ocean, you might guess that it is safe from the impact of humans, but you would be wrong. Scientists have found that, despite its depth and remoteness, the deep sea contains levels of toxins that match some of the most polluted marine systems on earth.
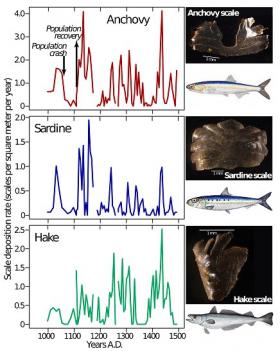
New Methods Further Discern Extreme Fluctuations in Forage Fish Populations
California sardine stocks famously crashed in John Steinbeck’s “Cannery Row.” New research, building on the pioneering work of Soutar and Isaacs in the late 1960’s and others, shows in greater detail that such forage fish stocks have undergone boom-bust cycles for centuries, with at least three species off the U.S. West Coast repeatedly experiencing steep population increases followed by declines long before commercial fishing began.
Natural population fluctuations in Pacific sardine, northern anchovy and Pacific hake off California have been so common that the species were in collapsed condition 29 to 40 percent of the time over the 500-year period from A.D. 1000 to 1500, according to the study published today in Geophysical Research Letters. Using a long time series of fish scales deposited in low-oxygen offshore sedimentary environments off southern California, the authors from NOAA Fisheries and the University of Michigan described such collapses as “an intrinsic property of some forage fish populations that should be expected, just as droughts are expected in an arid climate.”
How temperature guides where species live and where they'll go
For decades, among the most enduring questions for ecologists have been: "Why do species live where they do? And what are the factors that keep them there?" A Princeton University-based study featured on the February cover of the journal Ecology could prove significant in answering that question, particularly for animals in the world's temperate mountain areas.
Newly engineered material can cool roofs, structures with zero energy consumption
A team of University of Colorado Boulder engineers has developed a scalable manufactured metamaterial — an engineered material with extraordinary properties not found in nature — to act as a kind of air conditioning system for structures. It has the ability to cool objects even under direct sunlight with zero energy and water consumption.
When applied to a surface, the metamaterial film cools the object underneath by efficiently reflecting incoming solar energy back into space while simultaneously allowing the surface to shed its own heat in the form of infrared thermal radiation.