IN THE SUMMER months of 2015, Jeffrey Schnapp and a few of his colleagues started collecting rideables. The hoverboard craze was in full swing, and OneWheels and Boosteds were showing up on roads and sidewalks. Schnapp and his co-founders rode, drove, and crashed everything they could find. For Schnapp, a Harvard professor and longtime technologist with a shaved head, pointy goatee, and a distinct Ben Kingsley vibe, this was market research.
articles
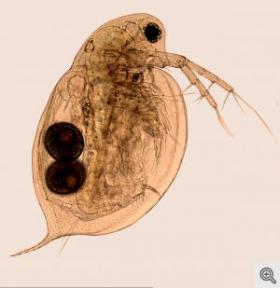
'Resurrecting' tiny lake-dwelling animals to study evolutionary responses to pollution
A University of Michigan biologist combined the techniques of "resurrection ecology" with the study of dated lake sediments to examine evolutionary responses to heavy-metal contamination over the past 75 years.
Study links outdoor air pollution with millions of preterm births
The study, which was led by a team from The Stockholm Environment Institute (SEI) at the University of York, found that in 2010, about 2.7 million preterm births globally – or 18% of all pre-term births – were associated with outdoor exposure to fine particulate matter.
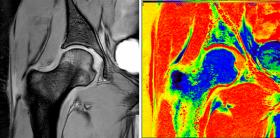
Real-Time MRI Analysis Powered by Supercomputers
One of the main tools doctors use to detect diseases and injuries in cases ranging from multiple sclerosis to broken bones is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). However, the results of an MRI scan take hours or days to interpret and analyze. This means that if a more detailed investigation is needed, or there is a problem with the scan, the patient needs to return for a follow-up.
Less snow and a shorter ski season in the Alps
After long-awaited snowfall in January, parts of the Alps are now covered with fresh powder and happy skiers. But the Swiss side of the iconic mountain range had the driest December since record-keeping began over 150 years ago, and 2016 was the third year in a row with scarce snow over the Christmas period. A study published today in The Cryosphere, a journal of the European Geosciences Union, shows bare Alpine slopes could be a much more common sight in the future.
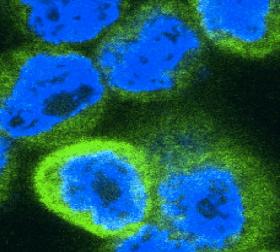
How cancers trick the immune system into helping rather than harming them
Scientists at Trinity College Dublin have discovered how certain cancers hijack the immune system for their benefit -- tricking it into helping rather than harming them.