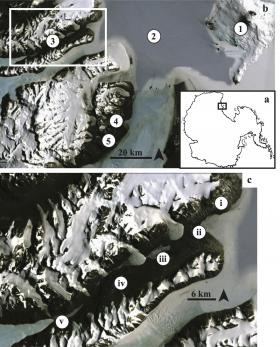
As climate change continues to impact the Antarctic, glacier melt and permafrost thaw are likely to make more liquid water available to soil and aquatic ecosystems in the McMurdo Dry Valleys, potentially providing a more nutrient-rich environment for life, according to a Dartmouth study recently published in Antarctic Science. (A pdf of the study is available upon request).
With an average annual air temperature of -2.2 F and an average precipitation of 3-50 mm per year, the McMurdo Dry Valleys of Antarctica are dominated by dry soils underlain by permafrost. The Dry Valleys ecosystem is severely limited by liquid water and nutrients, resulting in limited organic matter. One such limited nutrient is phosphorus, an element that is essential to all living organisms. Understanding the spatial distribution of phosphorus in the soil is crucial to identifying where life could become more abundant in the future.