Star Formation: Three scientists at Niels Bohr Institute (NBI), University of Copenhagen, have carried out extensive computer simulations related to star formation. They conclude that the present idealized models are lacking when it comes to describing details in the star formation process. “Hopefully our results can also help shed more light on planet formation”, says Michael Küffmeier, astrophysicist and head of the research team.
articles
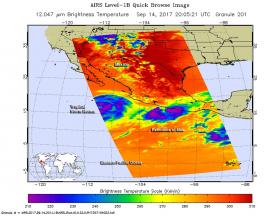
NASA Sees Hurricane Max Make Landfall and Weaken
NASA’s Aqua satellite captured in infrared-light image of Hurricane Max that showed the storm weakened quickly as it made landfall in southwestern Mexico. Max quickly degenerated into a large area of low pressure.
New Orleans Greenery Post-Katrina Reflects Social Demographics More Than Storm Impact
Popular portrayals of “nature reclaiming civilization” in flood-damaged New Orleans, Louisianna, neighborhoods romanticize an urban ecology shaped by policy-driven socioecological disparities in redevelopment investment, ecologists argue in a new paper in the Ecological Society of America’s open access journal Ecosphere.
Poor Sleep Hastens Progression of Kidney Disease
People with chronic kidney disease may be especially vulnerable to the deleterious effects of poor sleep, according to a new paper published in the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology.
Wolves Understand Cause and Effect Better Than Dogs
A rattle will only make noise if you shake it. Children learn this principle of cause and effect early on in their lives. However, animals like the wolf also understand such connections and are better at this than their domesticated descendants. Researchers at the Wolf Science Center of the Vetmeduni Vienna say that wolves have a better causal understanding than dogs and that they follow human-given communicative cues equally well. The study in Scientific Reports provides the insight that the process of domestication can also affect an animal’s causal understanding.
Skin Patch Dissolves "Love Handles" in Mice
Researchers have devised a medicated skin patch that can turn energy-storing white fat into energy-burning brown fat locally while raising the body’s overall metabolism. The patch could be used to burn off pockets of unwanted fat such as “love handles” and treat metabolic disorders, such as obesity and diabetes, according to researchers at Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) and the University of North Carolina.