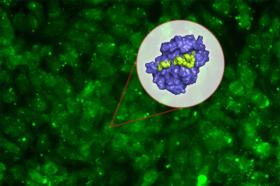
MIT biologists have designed a new peptide that can disrupt a key protein that many types of cancers, including some forms of lymphoma, leukemia, and breast cancer, need to survive.
articles
Weather anomalies accelerate the melting of sea ice
ETH researchers reveal why Arctic sea ice began to melt in the middle of winter two years ago – and that the increased melting of ice in summer is linked to recurring periods of fair weather.
Math Can Predict How Cancer Cells Evolve
Applied mathematics can be a powerful tool in helping predict the genesis and evolution of different types of cancers, a study from the University of Waterloo has found.
Asthma Costs the U.S. Economy More than $80 Billion Per Year
Asthma costs the U.S. economy more than $80 billion annually in medical expenses, missed work and school days and deaths, according to new research published online in the Annals of the American Thoracic Society.
Northern corn leaf blight genes identified in new study
Midwestern corn growers know the symptoms of northern corn leaf blight all too well: greenish-gray lesions on the leaves that can add up to major yield losses if not detected and treated early. Resistance genes have been identified in corn, but the fungal disease has found ways to sneak around corn’s defenses. Now, researchers have figured out how the fungus is outsmarting corn, and they may be able to use this information to help corn fight back.
“We were looking for genes in the fungus that trigger disease in corn. With this information, corn breeders could someday build more durable resistance in future hybrids,” says Santiago Mideros, plant pathologist in the Department of Crop Sciences at the University of Illinois.
Warming Signs: How Diminished Snow Cover Puts Species in Peril
The wolverine is highly adapted to life in a snowy world. It has thick fur and snowshoe-like feet, and it dens high in the mountains as a way to avoid predators that aren’t as nimble in deep snow and to provide its kits with insulation from the bitter high-elevation cold.