It has been a challenge at times to get well-heeled and sometimes highly influential people to care about climate change. After all, having a great deal of money can serve to insulate someone from problems that afflict those less fortunate. Food prices going up, for example, not that big a deal. Coastal areas flooding out, go somewhere else for vacation. Many of those at the top of the heap are finding that business-as-usual is working very well for them, thank you very much. Besides, they might have significant investments in industries that could be threatened by changing to a more sustainable model. Perhaps, what is needed to get their attention is something that hits closer to home. Here is an item in England’s The Telegraph that might fit the bill: Apparently, rising temperatures in areas like France, Italy and Spain are affecting the flavor of certain wines.
articles
Don't put old electronic items in the trash!
Chances are, many Americans received shiny, new gadgets for the holidays — meaning their old electronics will either collect dust in a closet somewhere or get tossed out.
These unwanted laptops, tablets and printers contribute to the enormous amount of electronic waste, or “e-waste,” that continually piles up in our landfills. According to the EPA, 3.4 million tons of tech gear was trashed in 2012, and unfortunately, only 12.5 percent of e-waste is currently recycled.
Road salt not good for streams
This is the time of year when it's not uncommon to see big trucks barreling down highways and streets spreading road salt.
Steve Corsi, a hydrologist with the U.S. Geological Survey, says that translates into high levels of chloride concentrations for rivers like the Milwaukee in Wisconsin or 18 other streams near urban areas in Illinois, Ohio, Colorado and several other states.
"At many of the streams, concentrations have now exceeded those that are harmful to aquatic life," he says.
Trawling makes for skinny fish
Trawling the seabed doesn't just remove some of the fishes living there; it also makes some of the survivors thinner and less healthy by forcing them to use more energy finding less nutritious food. That's the conclusion of a new paper published in Proceedings of the Royal Society B, based on the work Dr Andrew Frederick Johnson undertook while studying for his PhD at Bangor University.
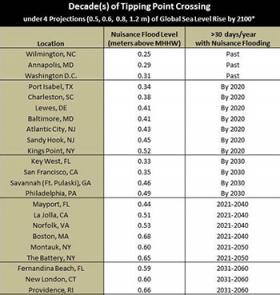
East Cost "nuisance" flooding already increasing
By 2050, much of U.S. coastal areas are likely to be threatened by 30 or more days of flooding annually because of dramatically accelerating impacts from sea-level rise, according to a new National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) study.
The findings appear in a paper entitled “From the Extreme to the Mean: Acceleration and Tipping Points for Coastal Inundation due to Sea Level Rise” and follows an earlier study by the report’s co-author, William Sweet, Ph.D., a NOAAA oceanographer.
Penguins Affected by Tourism in Antarctica
A trip to Antarctica might not be a dream vacation for everyone, but it’s on the list for many who are clearly willing to trek to there. While tourists are busy exploring the scenery and greeting the penguins who live there, scientists are raising concerns about how exposure to us could increase their risk of contracting infectious diseases. Scientists and disease experts believe the immune systems of penguins, and other species in the region, are less able to deal with pathogens that are commonplace in the rest of the world because they’ve been isolated for so long with few visitors.