A U of T Engineering innovation could make building printing cells as easy and inexpensive as printing a newspaper. Dr. Hairen Tan and his team have cleared a critical manufacturing hurdle in the development of a relatively new class of solar devices called perovskite solar cells. This alternative solar technology could lead to low-cost, printable solar panels capable of turning nearly any surface into a power generator.
articles
The Cute Robot That Follows You Around and Schleps All Your Stuff
IN THE SUMMER months of 2015, Jeffrey Schnapp and a few of his colleagues started collecting rideables. The hoverboard craze was in full swing, and OneWheels and Boosteds were showing up on roads and sidewalks. Schnapp and his co-founders rode, drove, and crashed everything they could find. For Schnapp, a Harvard professor and longtime technologist with a shaved head, pointy goatee, and a distinct Ben Kingsley vibe, this was market research.
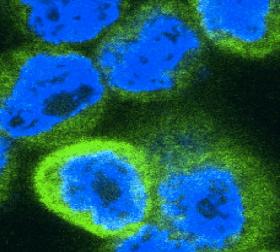
How cancers trick the immune system into helping rather than harming them
Scientists at Trinity College Dublin have discovered how certain cancers hijack the immune system for their benefit -- tricking it into helping rather than harming them.
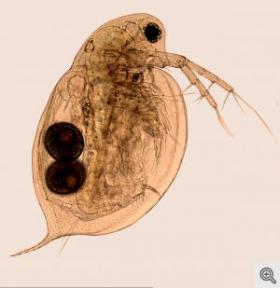
'Resurrecting' tiny lake-dwelling animals to study evolutionary responses to pollution
A University of Michigan biologist combined the techniques of "resurrection ecology" with the study of dated lake sediments to examine evolutionary responses to heavy-metal contamination over the past 75 years.
Study links outdoor air pollution with millions of preterm births
The study, which was led by a team from The Stockholm Environment Institute (SEI) at the University of York, found that in 2010, about 2.7 million preterm births globally – or 18% of all pre-term births – were associated with outdoor exposure to fine particulate matter.
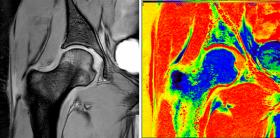
Real-Time MRI Analysis Powered by Supercomputers
One of the main tools doctors use to detect diseases and injuries in cases ranging from multiple sclerosis to broken bones is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). However, the results of an MRI scan take hours or days to interpret and analyze. This means that if a more detailed investigation is needed, or there is a problem with the scan, the patient needs to return for a follow-up.