Researchers from the University of California, Irvine and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory have reported the first observation of sea level “fingerprints,” tell-tale differences in sea level rise around the world in response to changes in continental water and ice sheet mass. The team’s findings were published today in the American Geophysical Union journal Geophysical Research Letters.
articles
Increasing Effective Decision-Making for Coastal Marine Ecosystems
Marine restoration, rather than protection, might be the most cost-effective solution for coastal marine ecosystems suffering from human activities, a new study has found.
Mediterranean-Style Diet May Eliminate Need for Reflux Medications
A plant-based, Mediterranean-style diet has been shown to provide the same medical benefits for treating laryngopharyngeal reflux as popular reflux medications. This is according to a study published today in JAMA Otolaryngology Head Neck Surgery by researchers from Northwell Health’s The Feinstein Institute for Medical Research and New York Medical College.
Hidden Inca Treasure: Remarkable New Tree Genus Discovered in the Andes
Hidden in plain sight – that’s how researchers describe their discovery of a new genus of large forest tree commonly found, yet previously scientifically unknown, in the tropical Andes.
Link Between Positive Emotions and Health Depends on Culture
Positive emotions are often seen as critical aspects of healthy living, but new researchsuggests that the link between emotion and health outcomes may vary by cultural context. The findings, published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, show that experiencing positive emotions is linked with better cardiovascular health in the US but not in Japan.
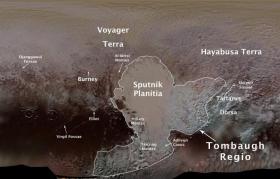
Pluto Features Given First Official Names
The IAU has assigned names to fourteen geological features on the surface of Pluto. The names pay homage to the underworld mythology, pioneering space missions, historic pioneers who crossed new horizons in exploration, and scientists and engineers associated with Pluto and the Kuiper Belt. This is the first set of official names of surface features on Pluto to be approved by the IAU, the internationally recognised authority for naming celestial bodies and their surface features.