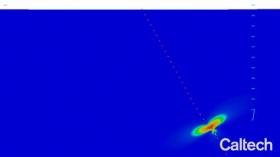
Glacier flow at the southern Antarctic Peninsula has increased since the 1990s, but a new study has found the change to be only a third of what was recently reported.
articles
Avian Flu Testing of Wild Ducks Informs Biosecurity and Can Reduce Economic Loss
Ducks in North America can be carriers of avian influenza viruses similar to those found in a 2016 outbreak in Indiana that led to the losses of hundreds of thousands of chickens and turkeys, according to a recent study.
Earthquakes Can Make Thrust Faults Open Violently and Snap Shut
It is a common trope in disaster movies: an earthquake strikes, causing the ground to rip open and swallow people and cars whole. The gaping earth might make for cinematic drama, but earthquake scientists have long held that it does not happen.
University of Toronto undergrad tests out solar-powered irrigation system in his native South Sudan
James Thuch Madhier fled South Sudan as a teenager, escaping the ravages of civil war and famine.
Next fall, the U of T undergrad and his social entrepreneurship team will be testing out their solar-powered crop irrigation system on 20 acres of land they've acquired in South Sudan.
Mice with missing lipid-modifying enzyme heal better after heart attack
Two immune responses are important for recovery after a heart attack — an acute inflammatory response that attracts leukocyte immune cells to remove dead tissue, followed by a resolving response that allows healing.
Protection of forests 'fundamental to security of humanity's place on this planet,' UN Forum told
Kick-starting action on the recently-adopted Global Forest Goals to protect, sustainably manage and increase world’s forest area will be a key focus for delegations gathered in New York for the twelfth session of the UN Forum on Forests, which opened today at United Nations Headquarters.