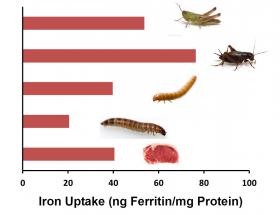
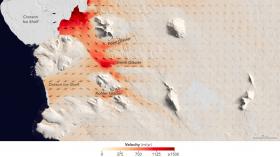
Scientists have detected high levels of a toxin produced by freshwater algae in mussels from San Francisco Bay. Although shellfish harvested from California's coastal waters are monitored for toxins produced by marine algae, they are not routinely tested for this freshwater toxin, called microcystin.
The toxin, which causes liver damage, is produced by a type of cyanobacteria (also known as blue-green algae) that thrives in warm, nutrient-rich water conditions. It has been found in many lakes and rivers in California, including the Sacramento and San Joaquin Rivers, which flow into the San Francisco Bay Delta, and in several Bay Area lakes.