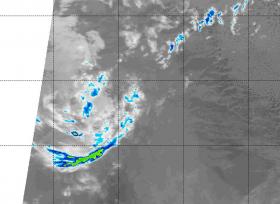
Former Hurricane Otis was not showing any thunderstorm development or precipitation on satellite imagery on Sept. 19. As a result, the National Hurricane Center declared Otis a remnant low pressure area.
articles
Vaping doubles risk of smoking cigarettes for teens
Teenagers who try e-cigarettes double their risk for smoking tobacco cigarettes, according to a new study.
The study — from the University of Waterloo and the Wake Forest School of Medicine — found that students in grades seven to 12 who had tried an e-cigarette are 2.16 times more likely to be susceptible to cigarette smoking.
Emerging Disease Further Jeopardizes North American Frogs
A deadly amphibian disease called severe Perkinsea infections, or SPI, is the cause of many large-scale frog die-offs in the United States, according to a new study by the U.S. Geological Survey.
Frogs and salamanders are currently among the most threatened groups of animals on the planet. The two most common frog diseases, chytridiomycosis and ranavirus infection, are linked to frog population declines worldwide. The new study suggests that that SPI is the third most common infectious disease of frogs.
Fuel from waste and electricity?
Technologies that allow the preservation of scarce fossil resources will pave the way towards resource security. The two main factors that contribute to a sustainable future industry are the source of electric energy and the carbon feedstock. First, the electrical power production based on renewable resources, such as wind and solar energy, is promoted. Second, renewable feedstocks and waste streams are considered as valuable precursors for the production of commodities and fuels. Building a bridge between both factors means linking the conversion of electric energy - especially from local peak productions - to chemical energy carriers and commodities. Researchers in a consortium led by Dr. Falk Harnisch from the UFZ show that this bridge can be build.
End-of-Summer Arctic Sea Ice Extent Is Eighth Lowest on Record
Arctic sea ice appeared to have reached its yearly lowest extent on Sept. 13, NASA and the NASA-supported National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) at the University of Colorado Boulder have reported. Analysis of satellite data by NSIDC and NASA showed that at 1.79 million square miles (4.64 million square kilometers), this year’s Arctic sea ice minimum extent is the eighth lowest in the consistent long-term satellite record, which began in 1978.
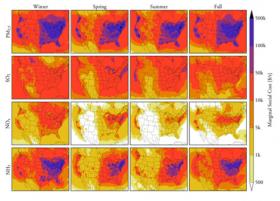
Putting the power to model pollution into your hands
At Carnegie Mellon, Professor Peter Adams is working to make sure that everyone who is affected by air pollution has the tools they need to understand the quality of their air. When we talk about studying air pollution, we typically think of official government agencies and university labs, measuring particles and tracking wind speed—and with good reason. Until very recently, modeling the movement of pollution in the air required very complex calculations—models that often took days and even weeks to run. But air quality affects everyone: not just governments and universities, but average citizens, children, pets. At Carnegie Mellon, Civil and Environmental Engineering (CEE) and Engineering and Public Policy (EPP) Professor Peter Adams is working to make sure that everyone who is affected by air pollution has the tools they need to understand the quality of their air.