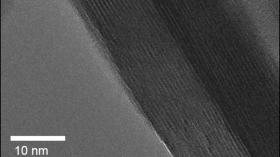
Researchers at North Carolina State University have found that a material which incorporates atomically thin layers of water is able to store and deliver energy much more quickly than the same material that doesn’t include the water layers. The finding raises some interesting questions about the behavior of liquids when confined at this scale and holds promise for shaping future energy-storage technologies.
articles
Weather extremes and trade policies were main drivers of wheat price peaks
Price peaks of wheat on the world market are mainly caused by production shocks such as induced for example by droughts, researchers found. These shocks get exacerbated by low storage levels as well as protective trade policies, the analysis of global data deriving from the US Department of Agriculture shows. In contrast to widespread assumptions, neither speculation across stock or commodity markets nor land-use for biofuel production were decisive for annual wheat price changes in the past four decades. This finding allows for better risk assessment. Soaring global crop prices in some years can contribute to local food crises, and climate change from burning fossil fuels and emitting greenhouse gases is increasing weather variability.
Ice cave in Transylvania yields window into region's past
Ice cores drilled from a glacier in a cave in Transylvania offer new evidence of how Europe's winter weather and climate patterns fluctuated during the last 10,000 years, known as the Holocene period.
The cores provide insights into how the region's climate has changed over time. The researchers' results, published this week in the journal Scientific Reports, could help reveal how the climate of the North Atlantic region, which includes the U.S., varies on long time scales.
Researchers discover safety feature in our perception of self motion
An international research collaboration between York University Faculty of Health Professor Laurence Harris and researchers in Japan has discovered that our perception of self motion has a previously unknown safety feature.
Teaching Perovskites to Swim
Harvesting sunlight and using it to power our homes and devices is a reality today. Generally, most commercial solar cells are made of silicon. However, as highlighted previously, a type of material called perovskite halides are a potential competitor of silicon. Unfortunately, most perovskite halides are sensitive to moisture and high temperatures such that exposure to either will quickly degrade these materials — rendering them useless. Researchers at the Argonne-Northwestern Solar Energy Research Center (ANSER) have developed a way to protect perovskites from water and stabilize them against heat. By carefully growing an ultrathin layer of metal oxide on a carbon coating, the researchers made a perovskite device that worked even after dousing the device with a stream of water.
Billions More Milkweeds Needed to Restore Monarchs
As many as 1.8 billion additional stems of milkweed plants may be needed in North America to return imperiled monarch butterflies to a sustainable population size, according to a recently published U.S. Geological Survey study.