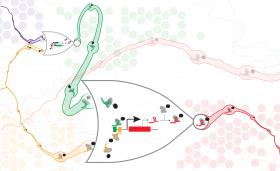
Living cells must constantly process information to keep track of the changing world around them and arrive at an appropriate response.
Through billions of years of trial and error, evolution has arrived at a mode of information processing at the cellular level. In the microchips that run our computers, information processing capabilities reduce data to unambiguous zeros and ones. In cells, it’s not that simple. DNA, proteins, lipids and sugars are arranged in complex and compartmentalized structures.
But scientists — who want to harness the potential of cells as living computers that can respond to disease, efficiently produce biofuels or develop plant-based chemicals — don’t want to wait for evolution to craft their desired cellular system.