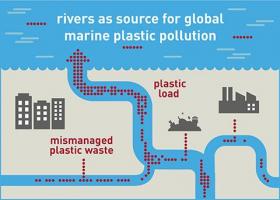
Every year, millions of tonnes of plastic debris ends up in the sea - a global environmental problem with unforeseeable ecological consequences. The path taken by plastic to reach the sea must be elucidated before it will be possible to reduce the volume of plastic input. To date, there was only little information available on this. It has now been followed up by an interdisciplinary research team who were able to show that plastic debris is primarily carried into the sea by large rivers.
articles
Is It Gonna Blow? Measuring Volcanic Emissions from Space
Carbon dioxide measured by a NASA satellite pinpoints sources of the gas from human and volcanic activities, which may help monitor greenhouse gases responsible for climate change.
Late last month, a stratovolcano in Bali named Mount Agung began to smoke. Little earthquakes trembled beneath the mountain. Officials have since evacuated thousands of people to prevent what happened when Agung erupted in 1963, killing more than 1,000 people.
Study suggests oysters offer hot spot for reducing nutrient pollution
When it comes to oysters and their role in reducing nutrient pollution, a new study by researchers at William & Mary’s Virginia Institute of Marine Science gets right to the guts—and the shell—of the matter.
New biomass plant to cut Simon Fraser University's greenhouse gases by two-thirds
A new project at Simon Fraser University (SFU) will soon divert wood waste from the landfill and help reduce greenhouse gasses at the University.
SFU and SFU Community Trust are collaborating with Corix Multi-Utility Services Inc., on a $33-million community-based biomass project called the Burnaby Mountain District Energy Utility (BMDEU).
Warming Seas Could Lead to 70 Percent Increase in Hurricane-related Financial Loss
If oceans warm at a rate predicted by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, the United Nation-sponsored group that assesses climate change research and issues periodic reports, expected financial losses caused by hurricanes could increase more than 70 percent by 2100, according to a University of Vermont study just published in the journal Sustainable and Resilient Infrastructure.
NOAA observing buoys validate findings from NASA's new satellite for measuring carbon dioxide
The strong El Niño event of 2015-2016 provided NASA and NOAA an unprecedented opportunity to test the effectiveness of the newest observation tool to measure global atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations -- NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 satellite or OCO-2.
Observations of carbon dioxide concentrations over the tropical Pacific from the satellite were validated by data from NOAA’s Tropical Pacific Observing System of buoys, which directly measure carbon dioxide concentrations at the surface of the ocean.