Climate change causes ecological variation and affects the lives of animals. The ever-earlier springs and later autumns caused by rising temperatures cause changes to animals’ physiology, breeding seasons and even population distributions. However, little is still known about how animals behave in response to these disturbances.
articles
Evidence shows increased risk of ozone loss over the United States in summer
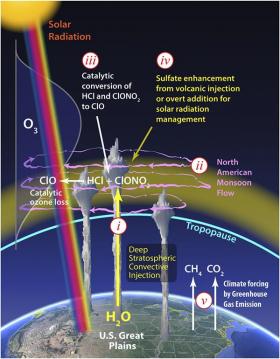
A new study out of Harvard University reveals that the protective stratospheric ozone layer above the central United States is vulnerable to erosion during the summer months from ozone-depleting chemical reactions, exposing people, livestock and crops to the harmful effects of UV radiation.
Powerful storm systems common to the Great Plains inject water vapor that, with observed temperature variations, can trigger the same chemical reactions over the central United States that are the cause of ozone loss over the polar regions, according to a new paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Mars' watery past
A new study led by Northern Illinois University geography professor Wei Luo calculates the amount of water needed to carve the ancient network of valleys on Mars and concludes the Red Planet’s surface was once much more watery than previously thought.
Decomposing Leaves Are A Surprising Source Of Greenhouse Gases
Michigan State University scientists have pinpointed a new source of nitrous oxide, a greenhouse gas that’s more potent than carbon dioxide. The culprit?
Tiny bits of decomposing leaves in soil.
This new discovery is featured in the current issue of Nature Geoscience, could help refine nitrous oxide emission predictions as well as guide future agriculture and soil management practices.
“Most nitrous oxide is produced within teaspoon-sized volumes of soil, and these so-called hot spots can emit a lot of nitrous oxide quickly,” said Sasha Kravchenko, MSU plant, soil and microbial scientist and lead author of the study. “But the reason for occurrence of these hot spots has mystified soil microbiologists since it was discovered several decades ago.”
Web-Based System for Self-Reporting Symptoms Helps Patients Live Longer
“Online technologies have transformed communications in practically every aspect of our lives, and now we’re seeing they’re also allowing patients to take an active role in their care and get immediate access to their care provider,” said ASCO Expert Harold J. Burstein, MD, PhD, FASCO. “It’s impressive that something as simple as this not only improves quality of life, but in this case, helps patients live longer. I think we’ll soon see more cancer centers and practices adopting this model.”
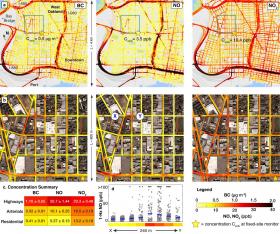
UT Austin, Environmental Defense Fund, Google and Aclima Unveil New Hyper-Local Air Pollution Map
Engineering researchers at The University of Texas at Austin have developed the most detailed and extensive local map of air pollution ever produced for an urban area, using specially equipped Google Street View cars to measure air quality on a block-by-block basis. This new hyper-local mobile approach to measuring air quality, which reveals that air pollution can vary dramatically even within a single city block, could address major air quality monitoring gaps worldwide.