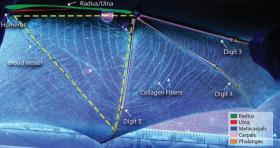
As more and more adults face old age alone, society needs to rethink its approach to health and elder care before this demographic shift puts further strain on an already taxed system, according to one Western researcher.
For most of human history, adults have generally been part of dense family networks who cared for them as they aged. But increasingly, adults are facing their ‘golden years’ without a spouse or children. This new living condition portends millions facing an absent support system in old age when care is generally assumed by one’s immediate family.