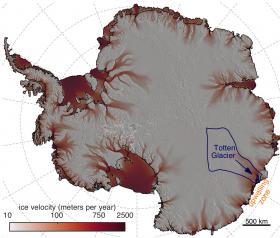
Totten Glacier, the largest glacier in East Antarctica, is being melted from below by warm water that reaches the ice when winds over the ocean are strong — a cause for concern because the glacier holds more than 11 feet of sea level rise and acts as a plug that helps lock in the ice of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet.
articles
NREL Research Yields Significant Thermoelectric Performance
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) reported significant advances in the thermoelectric performance of organic semiconductors based on carbon nanotube thin films that could be integrated into fabrics to convert waste heat into electricity or serve as a small power source.
Birmingham And East African Partners Lead The Battle On Air Pollution: Urban Africa's Silent Killer
An alliance of African and British experts are studying the growth of cities in East Africa in a bid to understand how to save lives at risk from air pollution – one of the biggest killers in urban Africa.
Led by the University of Birmingham, the international study looks at how rapid urbanisation in three African cities - Addis Ababa, Kampala and Nairobi impacts upon air quality.
‘A Systems Approach to Air Pollution in East Africa’ brings together leading UK and East African researchers in air pollution, urban planning, economic geography, public health, social sciences and development studies to provide a framework for improved air quality management in East African cities
Thinking Small
As eureka moments go, it didn’t entirely follow the script.
There was the flash of inspiration and a flush of excitement when a check of the literature showed that, yes, this could be the real deal.
Stanford Researchers Seek Citizen Scientists to Contribute to Worldwide Mosquito Tracking
It’s a sound that can keep even the weariest among us from falling asleep: the high-pitched whine of a mosquito. This irritating buzz already makes us run, slap and slather on repellant. But if Stanford University researchers have their way, it may also prompt us to take out our cellphones and do a little science.
She was born with heart defects. Now this researcher is looking for a cure
Bailey Bernknopf was born with four congenital heart defects.
She had her first surgery at five months old, followed by another at age 14 that had left doctors wondering if she would survive the night.