Exposed to light, plants turn green and form leaves. Not so in the dark. A signal responsible for this phenomenon has now been decoded.
articles
Cities Can Cut Greenhouse Gas Emissions Far Beyond Their Urban Borders
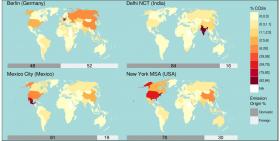
Greenhouse gas emissions caused by urban households’ purchases of goods and services from beyond city limits are much bigger than previously thought. These upstream emissions may occur anywhere in the world and are roughly equal in size to the total emissions originating from a city’s own territory, a new study shows. This is not bad news but in fact offers local policy-makers more leverage to tackle climate change, the authors argue in view of the UN climate summit COP23 that just started. They calculated the first internationally comparable greenhouse gas footprints for four cities from developed and developing countries: Berlin, New York, Mexico City, and Delhi. Contrary to common beliefs, not consumer goods like computers or sneakers that people buy are most relevant, but housing and transport – sectors that cities can substantially govern.
Why the Post-Paris Climate Challenge Is Even Harder Than We Thought
Climate negotiators gathering in Germany this week are still flush with the success of the Paris Agreement two years ago. But as they begin assembling a rule book for ensuring that the national pledges made in Paris are fulfilled, there comes a hard dose of reality. Those pledges, which constrain greenhouse gas emissions from now to 2030, will only deliver a third of the cuts needed to put the world on track to keep warming below the promised 2 degrees Celsius.
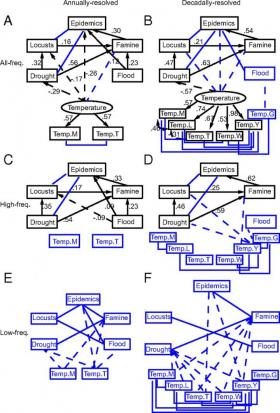
Biological Consequences of Climate Change on Epidemics May Be Scale-dependent
Conventional thinking holds that current climate warming will increase the prevalence and transmission of disease.
Relocating bus stops would cut riders' pollution exposure, UCLA study finds
oving bus stops away from intersections would substantially reduce the amount of pollution bus riders are exposed to, UCLA scientists report today in the journal Environmental Pollution.
Research has shown that in many cities in the United States and internationally, bus riders frequently spend 15 to 25 minutes or more each way waiting for a bus.
Circadian clock discovery could help boost water efficiency in food plants
A discovery by Texas A&M AgriLife Research scientists in Dallasprovides new insights about the biological or circadian clock, how it regulates high water-use efficiency in some plants, and how others, including food plants, might be improved for the same efficiency, possibly to grow in conditions uninhabitable for them today.