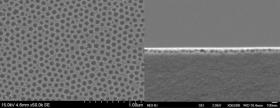
A team of chemists from the University of Kentucky and the Institute of Physics Research of Mar del Plata in Argentina has just reported a way to trigger a fundamental step in the mechanism of photosynthesis, providing a process with great potential for developing new technology to reduce carbon dioxide levels.
Led by Marcelo Guzman, an associate professor of chemistry in the UK College of Arts and Sciences, and Ruixin Zhou, a doctoral student working with Guzman, the researchers used a synthetic nanomaterial that combines the highly reducing power of cuprous oxide (Cu2O) with a coating of oxidizing titanium dioxide (TiO2) that prevents the loss of copper (I) ion in the catalyst. The catalyst made of Cu2O/TiO2 has the unique ability to transfer electrons for reducing the atmospheric greenhouse gas carbon dioxide (CO2) while simultaneously breaking the molecule of water (H2O). The unique feature of this catalyst for electron transfer mimics the so called “Z-scheme” mechanism from photosynthesis.