According to Einstein’s theory of General Relativity when a ray of light passes close to a very massive object, the gravity of the object attracts the photons and deviates them from their intial path. This phenomenon, known as gravitational lensing, is comparable to that produced by lenses on light rays, and acts as a sort of magnifier, changing the size and intensity of the apparent image of the original object.
articles
The last survivors on Earth
The world’s most indestructible species, the tardigrade, an eight-legged micro-animal, also known as the water bear, will survive until the Sun dies, according to a new Oxford University collaboration.
CEO Says Mexico Oil Find Is 'Multiples Of What We Thought'
It’s been a few years of soul-searching for Tim Duncan, the CEO of Talos Energy. The Houston-based oil company has long specialized in the shallow waters of the Gulf of Mexico off Louisiana and Texas. Yet the oil bust that began in 2014 has made the region deeply unpopular. Facing dwindling prospects for big new finds offshore, companies have instead flocked to the Permian basin of west Texas, where layer upon layer of oil-saturated rock promises decent returns even at stubbornly low oil prices.
“We resisted the temptation to join the land race onshore,” says Duncan. But Talos did go somewhere new: Mexico.
Unabated climate change would reverse the development gains in Asia: report
Unabated climate change would bring devastating consequences to countries in Asia and the Pacific, which could severely affect their future growth, reverse current development gains, and degrade quality of life, according to a report produced by the Asian Development Bank (ADB) and the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK).
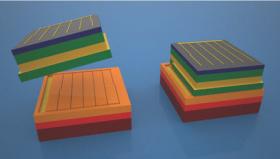
Scientists Design Solar Cell That Captures Nearly All Solar Spectrum Energy
A SEAS researcher helped develop technology that could become the most efficient solar cell in the world.
Severe weather model predicted tornado's path hours before it formed
As severe weather brewed in the Texas panhandle late in the afternoon of May 16, NOAA’s National Weather Service forecasters alerted residents in parts of western Oklahoma about the potential for large hail and damaging tornadoes that evening, particularly in the area around Elk City.
Ninety minutes later, a dangerous, rain-wrapped EF2 tornado struck the small town. It killed one, injured eight and destroyed about 200 homes and more than 30 businesses.