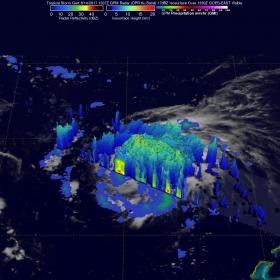
NASA looked at the rainfall rates within Tropical Storm Gert as it continued to strengthen and found the most intense rainfall on the tropical cyclone's eastern side. Just over 12 hours later, Gert would strengthen into a hurricane. As Gert has strengthened, the storm began generating dangerous surf along the U.S. East coast.
The Global Precipitation Measurement mission or GPM core observatory satellite passed above tropical storm Gert on August 14, 2017 at 9:36 a.m. EDT (1336 UTC) when winds had reached about 57.5 mph (50 knots). Data collected by GPM's Microwave Imager (GMI) and Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) instruments were used to show the coverage and the intensity of rainfall around Tropical Storm Gert. The area covered by GPM's radar swath revealed that the most intense rainfall, measuring greater 3.5 inches (90 mm) per hour, was located in bands of rain on the eastern side of the storm.