When it is cold in winter, cars tend to have starting problems. This is not much better with electric cars, which inevitably lose capacity of their rechargeable lithium-ion batteries at freezing temperatures. Now, Chinese scientists have offered a strategy to avoid plunging battery kinetics. In a study published in the journal Angewandte Chemie, they designed a battery system with a cold-enduring hard-carbon anode and a powerful lithium-rich cathode, with the important initial lithiation step integrated.
articles
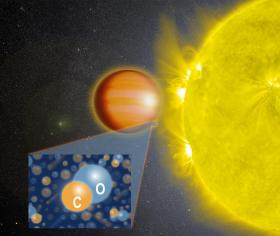
WASP-18b Has Smothering Stratosphere Without Water
A NASA-led team has found evidence that the oversized planet WASP-18b is wrapped in a smothering stratosphere loaded with carbon monoxide and devoid of water. The findings come from a new analysis of observations made by the Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes.
Augmented-Reality Technology Could Help Treat 'Lazy Eye'
When signals between the brain and one eye go awry, input from the other eye can become predominant, a condition called amblyopia or “lazy eye.” Amblyopia is common and it is typically treated by forcing the less dominant eye to adapt, either through lab-based training or wearing an eyepatch. But new research suggests that people may be able to use wearable augmented-reality technology to reduce this visual discrepancy as they go about everyday activities.
Beyond Wind Speed: A New Measure for Predicting Hurricane Impacts
Six major hurricanes that engulfed the Atlantic Basin in 2017 were a devastating reminder of the vulnerability of coastal communities, where more than half the U.S. population resides.
Study Finds Variation Within Species is a Critical Aspect of Biodiversity
Concerns about biodiversity tend to focus on the loss of species from ecosystems, but a new study suggests that the loss of variation within species can also have important ecological consequences.
Obesity Prevented in Mice Fed High-Fat Diet
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have identified a way to prevent fat cells from growing larger, a process that leads to weight gain and obesity. By activating a pathway in fat cells in mice, the researchers found they could feed the animals a high-fat diet without making them obese.