Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, is one of our solar system’s most intriguing and Earth-like bodies. It is nearly as large as Mars and has a hazy atmosphere made up mostly of nitrogen with a smattering of organic, carbon-based molecules, including methane (CH4) and ethane (C2H6). Planetary scientists theorize that this chemical make-up is similar to Earth’s primordial atmosphere.
articles
Lights! Action! Photo-Activated Catalyst Grabs CO2 to Make Ingredients for Fuel
Scientists have developed a light-activated material that can chemically convert carbon dioxide into carbon monoxide without generating unwanted byproducts. The achievement marks a significant step forward in developing technology that could help generate fuel and other energy-rich products using a solar-powered catalyst while mitigating levels of a potent greenhouse gas.
LSUHealthNO Research Finds Walnuts May Promote Health by Changing Gut Bacteria
Research led by Lauri Byerley, PhD, RD, Research Associate Professor of Physiology at LSU Health New Orleans School of Medicine, has found that walnuts in the diet change the makeup of bacteria in the gut, which suggests a new way walnuts may contribute to better health. The findings are published in The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry available online.
Computer models provide new understanding of sickle cell disease
Computer models developed by Brown University mathematicians show new details of what happens inside a red blood cell affected by sickle cell disease. The researchers said they hope their models, described in an article in the Biophysical Journal, will help in assessing drug strategies to combat the genetic blood disorder, which affects millions of people worldwide.
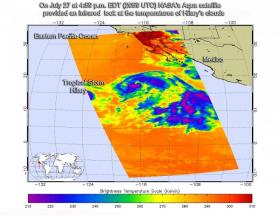
NASA Sees Hilary Weaken to Tropical Storm Status
NASA’s Aqua satellite provided infrared imagery Hurricane Hilary that showed it weakening. Within 12 hours the storm weakened to a tropical storm.
NASA's Aqua Satellite Tracks Typhoon Nesat Headed Toward Taiwan
NASA’s Aqua satellite passed over Typhoon Nesat as the storm continued moving north toward Taiwan.