Financial aid to fisheries in developing countries has declined by 30 percent, finds a new study from UBC and Stockholm Resilience Centre researchers, published in Marine Policy. Projects focusing on climate issues in fisheries had a 77 percent decline over the five years studied.
articles
Ocean Waters Prevent Release of Ancient Methane
Ocean sediments are a massive storehouse for the potent greenhouse gas methane.
Coping With Climate Stress in Antarctica
Some Antarctic fish living in the planet’s coldest waters are able to cope with the stress of rising carbon dioxide levels in the ocean. They can even tolerate slightly warmer waters. But they can’t deal with both stressors at the same time, according to a study from the University of California, Davis.
Reimbursing Ranchers for Livestock Killed by Predators Supports Conservation Efforts
Alberta’s predator compensation program offsets costs of conserving wildlife habitat on private lands in the province.
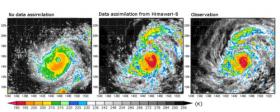
Himawari-8 data assimilated simulation enables 10-minute updates of rain and flood predictions
Using the power of Japan’s K computer, scientists from the RIKEN Advanced Institute for Computational Science and collaborators have shown that incorporating satellite data at frequent intervals—ten minutes in the case of this study—into weather prediction models can significantly improve the rainfall predictions of the models and allow more precise predictions of the rapid development of a typhoon.
NASA IMERG Reveals Rainfall Rates of Tropical Cyclone Berguitta
Heavy rain surrounded Tropical Cyclone Berguitta as it continued to move toward the island of Mauritius in the Southern Indian Ocean. NASA calculated the rate in which rain was falling within the hurricane-strength storm in the Southern Indian Ocean.