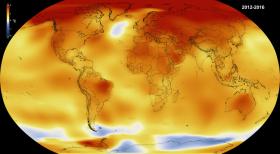
Global surface temperatures surged by a record amount from 2014 to 2016, boosting the total amount of warming since the start of the last century by more than 25 percent in just three years, according to new University of Arizona-led research.
articles
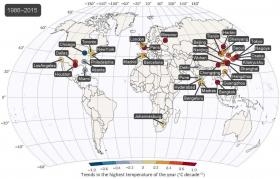
Rise in severity of hottest days outpaces global average temperature increase
UCI study also finds megacities affected most by uptick in extreme-heat events
Less predictable precipitation
Waning influence of once-telling weather patterns altered by global warming skews projections.
York University research explains why global responses to pandemics are too slow
New research out of York University shows that political dilly-dallying delays global responses to emerging pandemics more than poor surveillance capacity.
Steven J. Hoffman, professor in the Dahdaleh Institute for Global Health Research, Faculty of Health and Osgoode Hall Law School and his colleague Sarah L. Silverberg, conducted an analysis of the three most recent pandemics – H1N1, Ebola and Zika. These were used as case studies to identify and compare sources of delays in responding to pandemics and examine what influences the length of delays.
Rare Traces of a Volatile Gas
Nitrogen oxides — i.e. nitrogen compounds with varying amounts of oxygen — have a very bad reputation. They are produced among other things by burning fossil fuels. In regions with heavy traffic and a lot of industry, they occur in high concentrations and are made responsible for a large number of diseases of the respiratory system. However, nitrogen oxides also occur in nature. There they play an important role in the nitrogen cycle, which ensures that nitrogen, essential for life, is available in forms that the organisms can process.
Meat is not the "new tobacco," and shouldn't be taxed
The idea of having to pay a sin tax for environmentally detrimental foods is gaining more support. For some, eating meat is a sin, and therefore meat products should be taxed like alcohol and tobacco.
A new report published recently by a British group called Farm Animal Investment Risk and Return Initiative (FAIRR) argues that a tax on meat is inevitable.