Marine bacteria that live in the dark depths of the ocean play a newly discovered and significant role in the global carbon cycle, according to a new study published in Science.
articles
Breakthrough in tornado short-term forecasting could mean earlier, more accurate warnings
When mere seconds of storm warning could mean the difference between harm or safety, two researchers with Western University ties have developed a tornado-prediction method they say could buy as much as 20 minutes more warning time.
The health threat from mercury in freshwater fish could be blowing away in the wind
Mercury is one of the top 10 chemical concerns for public health according to the World Health Organization (WHO). In more than half of Swedish lakes the mercury levels are so high that eating the fish is a threat to the health of people and wildlife. To make matters worse, the problem seems to have no solution in sight. But new research gives hope: the mercury problem could very well be blowing away in the wind.
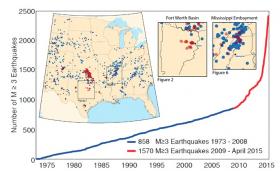
SMU seismology research shows North Texas earthquakes occurring on “dead” faults
Study by Beatrice Magnani, USGS and other SMU scientists shows recent seismicity in Fort Worth Basin occurred on faults not active for 300 million years.
New Technique Can Detect Impurities in Ground Beef Within Minutes
Researchers at the University of British Columbia have found a better way to identify unwanted animal products in ground beef.
Fear of Sharks Influences Seaweed Growth on Fijian Coral Reefs
Fishes’ fear of sharks helps shape shallow reef habitats in the Pacific, according to new research by a scientist at Bigelow Laboratory for Ocean Sciences.