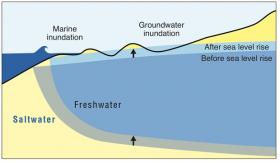
New research from the University of HawaiÊ»i at MÄnoa reveals a large part of the the heavily urbanized area of Honolulu and WaikÄ«kÄ« is at risk of groundwater inundation—flooding that occurs as groundwater is lifted above the ground surface due to sea level rise. Shellie Habel, lead author of the study and doctoral student in the Department of Geology and Geophysics, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), and colleagues developed a computer model that combines ground elevation, groundwater location, monitoring data, estimates of tidal influence and numerical groundwater-flow modeling to simulate future flood scenarios in the urban core as sea level rises three feet, as is projected for this century under certain climate change scenarios.
New research from the University of HawaiÊ»i at MÄnoa reveals a large part of the the heavily urbanized area of Honolulu and WaikÄ«kÄ« is at risk of groundwater inundation—flooding that occurs as groundwater is lifted above the ground surface due to sea level rise. Shellie Habel, lead author of the study and doctoral student in the Department of Geology and Geophysics, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), and colleagues developed a computer model that combines ground elevation, groundwater location, monitoring data, estimates of tidal influence and numerical groundwater-flow modeling to simulate future flood scenarios in the urban core as sea level rises three feet, as is projected for this century under certain climate change scenarios.
“This flooding will threaten $5 billion of taxable real estate; flood nearly 30 miles of roadway; and impact pedestrians, commercial and recreation activities, tourism, transportation and infrastructure,” said Habel. “The flooding will occur regardless of seawall construction, and thus will require innovative planning and intensive engineering efforts to accommodate standing water in the streets.”
Continue reading at University of Hawaii At Manoa
Image: Sea level rise lifts freshwater, causing groundwater inundation in low-lying areas. Credit: UH MÄnoa Coastal Geology Group.