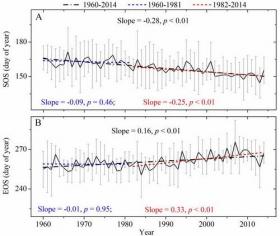
How vegetation phenology on the Tibetan Plateau (TP), the earth's largest surface area above 4000 m ASL, responds to climate change, in particular to rising temperatures, has attracted much attention in recent years. An increase in growth activity of high-elevation vegetation on the TP may have a considerable impact on the regional carbon budget.
>> Read the Full Article

Fusion power has the potential to provide clean and safe energy that is free from carbon dioxide emissions. However, imitating the solar energy process is a difficult task to achieve. Two young plasma physicists at Chalmers University of Technology have now taken us one step closer to a functional fusion reactor. Their model could lead to better methods for decelerating the runaway electrons, which could destroy a future reactor without warning.
>> Read the Full Article

Researcher Catherine Trask and recent master’s graduate Xiaoke Zeng have found that farmers experience prolonged “body shock” when riding horses or driving farming machinery on uneven terrain during an average workday. Whole body vibration is a major risk factor for developing back pain, they say.
“Farmers are often unaware that body vibration from machinery use is a potentially harmful physical hazard,” said Trask, U of S Canada Research Chair in Ergonomics and Musculoskeletal Health
>> Read the Full Article

Two antimicrobial chemicals already banned in antiseptic wash products by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration are still found in more than 2,000 widely used consumer products, despite offering no health benefits and actually causing health and environmental harm, according to more than 200 scientists and medical professionals.
>> Read the Full Article

Plant diseases pose a serious threat to global food security, especially in developing countries, where millions of people depend on consuming what they harvest.
In sub-Saharan Africa, one plant disease in particular – maize lethal necrosis – is ravaging one of the region's preferred crops for food, feed and income. But understanding its biology in order to manage the disease is difficult because the disease arises from two viruses interacting – which is where mathematics comes into play.
>> Read the Full Article
Most cars and trucks in the United States run on a blend of 90 percent gasoline and 10 percent ethanol, a renewable fuel made primarily from fermented corn. But producing the 14 billion gallons of ethanol consumed annually by American drivers requires millions of acres of farmland.
A recent discovery by Stanford University scientists could lead to a new, more sustainable way to make ethanol without corn or other crops. This technology has three basic components: water, carbon dioxide and electricity delivered through a copper catalyst. The results are published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
>> Read the Full Article

Three million measurement points in one square kilometer: Prof. Xiaoxiang Zhu and her team have set a world record in information retrieval from satellite data. Thanks to new algorithms, the researchers from the Technical University of Munich (TUM) succeeded in making four-dimensional point clouds of Berlin, Las Vegas, Paris and Washington, D.C. from images stacks of the TerraSAR-X radar satellite. Next the scientists plan to create four-dimensional models of all cities in the world.
>> Read the Full Article

The Yosemite toad (Anaxyrus canorus) is a rare species found exclusively in California's Sierra Nevada. While its range encompasses hundreds of miles, spanning five national forests and two national parks, the livelihood and future survival of this federally threatened species may come down to mere centimeters.
According to research by the U.S. Forest Service's Pacific Southwest Research Station and its collaborators, for pools within alpine meadows to be suitable habitat for laying eggs and sustaining tadpoles, little things mean a lot.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment