Detecting and predicting lightning just got a lot easier. The first images from a new instrument onboard NOAA’s GOES-16 satellite are giving NOAA National Weather Service forecasters richer information about lightning that will help them alert the public to dangerous weather.
Detecting and predicting lightning just got a lot easier. The first images from a new instrument onboard NOAA’s GOES-16 satellite are giving NOAA National Weather Service forecasters richer information about lightning that will help them alert the public to dangerous weather.
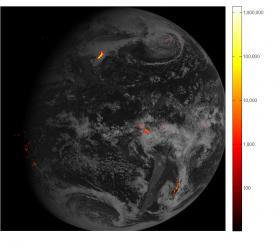
The first lightning detector in a geostationary orbit, the Geostationary Lightning Mapper (GLM), is transmitting data never before available to forecasters. The mapper continually looks for lightning flashes in the Western Hemisphere, so forecasters know when a storm is forming, intensifying and becoming more dangerous. Rapid increases of lightning are a signal that a storm is strengthening quickly and could produce severe weather.
During heavy rain, GLM data will show when thunderstorms are stalled or if they are gathering strength. When combined with radar and other satellite data, GLM data may help forecasters anticipate severe weather and issue flood and flash flood warnings sooner. In dry areas, especially in the western United States, information from the instrument will help forecasters, and ultimately firefighters, identify areas prone to wildfires sparked by lightning.
Continue reading at NOAA.
Photo via NOAA.